The quest for natural cognitive enhancers has led to the exploration of various compounds with potential nootropic properties.
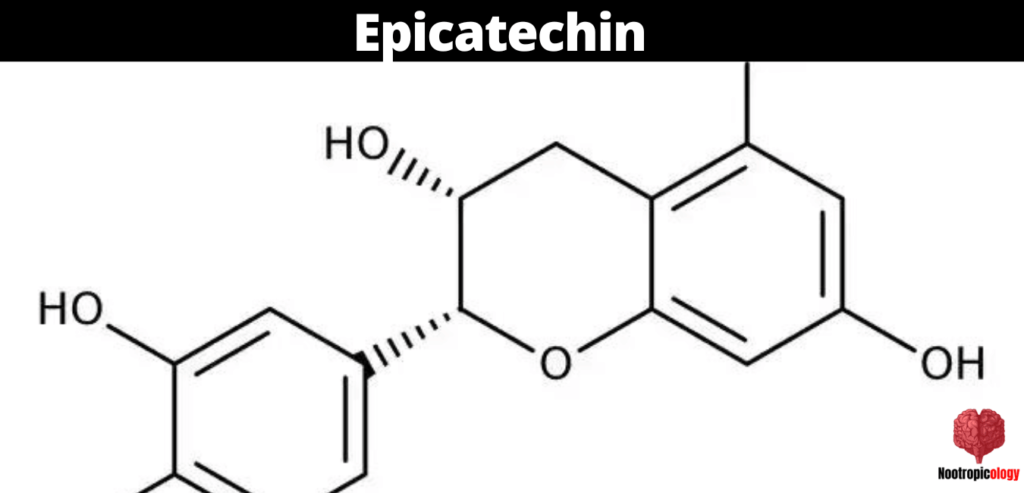
In my examination of this evolving field, Epicatechin has emerged as an intriguing bioactive flavonoid.
Renowned for its presence in cocoa beans, green tea, and certain fruits, Epicatechin's characteristics and potential benefits as a nootropic warrant a closer look.
Quick Overview of Epicatechin as a Nootropic:
- Flavonoid Classification: Epicatechin belongs to the flavanol subclass of flavonoids, a group of phytonutrients known for their diverse biological activities. Its molecular structure aligns with other catechins, giving it specific biochemical properties.
- Antioxidant Properties: In my investigation, I've found that one of Epicatechin's key bioactive features is its antioxidant capacity. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, it may offer protection against neurodegenerative conditions.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The potential anti-inflammatory effects of Epicatechin further contribute to its nootropic appeal. Inflammation is associated with cognitive decline, and Epicatechin may act on specific pathways to mitigate this process.
- Blood Flow Enhancement: Epicatechin appears to have vasodilatory effects, promoting blood flow in various tissues, including the brain. This aspect of its bioactivity could have implications for cognitive function, as increased blood flow can enhance oxygen and nutrient delivery to brain cells.
The above characteristics form the foundation for the more detailed exploration that follows below, where I'll delve into specific aspects such as neuroprotection, memory enhancement, and safety considerations.
So without further ado, let's dive in, shall we?
Epicatechin's Neuroprotective Effects
The neuroprotective properties of Epicatechin are multifaceted, encompassing antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, enhancement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and potential modulation of autophagy.[1]
Antioxidant Activity in Neuroprotection
Epicatechin's role as an antioxidant within the neural environment plays a key part in its neuroprotective capacity. Its ability to scavenge free radicals and neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) is vital in combating oxidative stress, a significant contributor to neurodegeneration.[2]
This protective mechanism plays a pivotal role in slowing the pathogenesis of oxidative stress-induced neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Brain
The anti-inflammatory action of Epicatechin represents another dimension of its neuroprotective profile. By inhibiting the Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a central mediator of inflammation in the brain, Epicatechin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.[3]
This could have profound implications for neural health, especially in conditions characterized by chronic neuroinflammation.
Enhancement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
The potential enhancement of BDNF by Epicatechin has aroused considerable interest. BDNF is vital for neuroplasticity, synaptic strength, memory, learning, and overall cognitive function.[4]
The possible elevation of BDNF levels by Epicatechin offers a promising avenue for therapeutic intervention in cognitive disorders such as depression and dementia.
Impact of Epicatechin on Blood Flow and Vasodilation
Blood flow and vasodilation are critical to overall health, and especially to cognitive function, as they determine the amount of oxygen and nutrients delivered to the brain.
Epicatechin's impact on these physiological processes is a vital aspect of its potential as a nootropic. Let's take a closer look below:
Effects on Nitric Oxide Production
Nitric oxide (NO) plays a crucial role in vasodilation, and Epicatechin has been found to enhance NO production. By stimulating the activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), Epicatechin may increase the bioavailability of NO in the vascular system.[5]
This can lead to improved blood flow, especially in microcirculation, which includes the delicate blood vessels within the brain.
Enhanced cerebral blood flow provides more oxygen and glucose to the brain, supporting cognitive function. Epicatechin's vasodilatory effect leads to increased cerebral perfusion, enhancing mental clarity, focus, and overall cognitive performance.
Potential Protection Against Vascular Diseases
Epicatechin's ability to improve blood flow and vasodilation might have protective effects against various vascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis. By promoting a healthy vascular endothelium, it can prevent the development of chronic conditions that could impair cognitive function over time.
One study investigated the effects of 28 days of low epicatechin dosing (1 mg/kg/day) on the cardiovascular function of deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats.[6]
The main points drawn from this study are:
- Myocardial Stiffness and Left Ventricular Compliance: Treatment with epicatechin attenuated the increase in myocardial stiffness and the significant reduction in left ventricular compliance observed in the DOCA control group. This suggests that epicatechin had a beneficial effect on cardiac compliance in hypertrophied DOCA-salt rat hearts.
- Reduction in Blood Pressure: The DOCA + E rats (those treated with epicatechin) exhibited a significant reduction in blood pressure. This aligns with previous findings about epicatechin's vasodilatory effects and its ability to improve nitric oxide levels.
- Decrease in Oxidative Stress: Malondialdehyde concentrations, a marker for oxidative stress, were significantly reduced in the DOCA + E group, indicating a potential antioxidant effect of epicatechin.
- No Improvement in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy, Electrophysiology, or Vascular Function: Despite the positive effects mentioned above, the study did not find improvements in left ventricular hypertrophy, electrophysiology, or vascular function in the rats treated with epicatechin.
The study concluded that epicatechin has the ability to reduce blood pressure, prevent myocardial stiffening, and preserve cardiac compliance in hypertrophied DOCA-salt rat hearts, but it did not affect left ventricular hypertrophy, electrophysiology, or vascular function.
Other Potential Nootropic Benefits of Epicatechin
While the primary focus has been on Epicatechin's neuroprotective effects, memory enhancement, and influence on blood flow and vasodilation, this compound has additional nootropic benefits worth examining.
- Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, and their proper functioning is vital for energy production. Some studies have suggested that Epicatechin enhances mitochondrial efficiency, possibly leading to increased energy levels and mental stamina.[7]
- Potential Improvement of Mood Disorders: Emerging research has hinted at the potential of Epicatechin in modulating mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Though the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, this avenue opens the door to a new set of applications for Epicatechin as a nootropic.[8]
Interactions with Other Nootropic Compounds
The interaction of Epicatechin with other nootropic compounds is an intriguing area of research.
While the literature on specific synergistic relationships between Epicatechin and other nootropics might not be extensive, some potential interactions can be inferred from its known mechanisms of action and shared pathways with other cognitive-enhancing substances.
Let's look at those below...
L-Theanine
L-Theanine, found in tea leaves, may work synergistically with Epicatechin, also found in green tea. L-Theanine is known to promote relaxation without sedation and may complement Epicatechin's effects on blood flow and neuroprotection.
Caffeine
Caffeine's stimulatory effects might pair well with Epicatechin's vasodilatory properties. Combining Epicatechin with caffeine could potentially enhance focus and energy levels, and this combination is naturally found in some cocoa and tea products.
Ginkgo Biloba
Ginkgo Biloba has been studied for its effects on memory and cognitive function and may interact positively with Epicatechin's neuroprotective and memory-enhancing properties.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. These might complement Epicatechin's similar properties, providing a more comprehensive approach to cognitive wellness.
Bacopa Monnieri
Bacopa Monnieri has been used traditionally for improving memory and may work synergistically with Epicatechin in enhancing memory formation and recall.
It's essential to recognize that these interactions are speculative and based on the combined potential benefits of Epicatechin and other nootropics rather than specific studies exploring their combined effects. Further research and clinical trials are needed to fully understand and validate these potential interactions and synergies.
Safety and Dosage Recommendations for Epicatechin as a Nootropic

The potential benefits of Epicatechin make it an exciting subject for nootropic enthusiasts and researchers alike.
However, understanding its safety profile and appropriate dosing is vital for responsible use and maximizing potential benefits.
Safety Considerations
- General Tolerance: Epicatechin, found in common foods like green tea and cocoa, is generally considered safe for consumption. However, specific concerns may arise with concentrated supplementation.
- Potential Interactions with Medications: As with many substances, Epicatechin may interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood pressure or cardiovascular function. Consulting with healthcare providers is advisable.
- Side Effects: At typical dietary levels, Epicatechin is unlikely to cause significant side effects. In higher supplemental doses, mild gastrointestinal disturbances might occur.
Nootropic Dosage Recommendation
- Dietary Sources: Consuming Epicatechin through dietary sources like dark chocolate or green tea is a common and generally safe way to obtain this compound.
- Supplemental Forms: The study mentioned earlier used a dosage of 1 mg/kg/day in hypertensive rats, but translating this to human dosing requires careful consideration. Human trials with Epicatechin have varied significantly in dosage, ranging from 25 to 200 mg per day.
- Targeted Uses: The appropriate dosage may depend on the specific nootropic goal, such as enhancing memory, improving blood flow, or providing neuroprotection. A personalized approach under the guidance of healthcare professionals would be advisable.
- Synergistic Combinations: When combined with other nootropics, the dosage of Epicatechin may need adjustment. Monitoring for potential additive effects or unexpected interactions would be essential.
Epicatechin's safety and dosage profile aligns with its status as a naturally occurring compound in commonly consumed foods.
Yet, when pursuing therapeutic or enhanced nootropic effects, caution, personalization, and professional guidance are recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What specific cognitive functions does Epicatechin enhance?
Epicatechin has been shown to enhance memory and learning capabilities. In some animal studies, it has been linked to improved spatial memory and increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
How does Epicatechin interact with other common nootropics like L-Theanine?
Research on specific interactions between Epicatechin and other nootropics like L-Theanine is limited. However, Epicatechin's effects on blood flow and neuroprotection might synergize with L-Theanine's calming effects to enhance overall cognitive function.
What's the recommended dosage of Epicatechin for cognitive enhancement?
Specific dosages for cognitive enhancement are not well-established, but general supplementation ranges from 50mg to 250mg per day. Clinical studies and personalized consultation with a healthcare provider are advisable for precise dosing.
Can Epicatechin be part of a nootropic stack, and with what other compounds?
Yes, Epicatechin can be part of a nootropic stack. Though specific studies are limited, it may be paired with compounds like caffeine to enhance alertness, or Ginkgo Biloba for increased blood flow and cognitive function.
My Thoughts on Epicatechin as a Nootropic
(−)-Epicatechin, found in foods like green tea and cocoa, has intrigued me with its potential as a nootropic. Research suggests promising benefits such as neuroprotective effects and memory enhancement, making it a compelling subject for cognitive improvement.
Its possible synergistic interactions with other nootropics like L-Theanine and caffeine add another dimension to its appeal, though more research is needed to fully understand these relationships.
What sets Epicatechin apart for me is its accessibility in everyday dietary sources and a generally favorable safety profile. However, caution with concentrated supplementation and personalized guidance from healthcare professionals is advisable.
While current knowledge on Epicatechin's nootropic benefits is promising, many questions remain unanswered. The complex nature of this compound, coupled with its versatility, makes it worthy of continued study and responsible exploration in the world of cognitive enhancement.
The insights gained from investigating Epicatechin have both broadened my perspective on nootropics and emphasized the importance of a thoughtful, evidence-based approach.
- Stringer, T P et al. “Plant-derived flavanol (-)epicatechin mitigates anxiety in association with elevated hippocampal monoamine and BDNF levels, but does not influence pattern separation in mice.” Translational psychiatry vol. 5,1 e493. 6 Jan. 2015, doi:10.1038/tp.2014.135
- Ashok, Anushruti et al. “Antioxidant Therapy in Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Clinical Translation.” Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,2 408. 17 Feb. 2022, doi:10.3390/antiox11020408
- Prince, Paula Denise et al. “Dietary (-)-epicatechin affects NF-κB activation and NADPH oxidases in the kidney cortex of high-fructose-fed rats.” Food & function vol. 10,1 (2019): 26-32. doi:10.1039/c8fo02230e
- Haskell-Ramsay, Crystal F et al. “The Impact of Epicatechin on Human Cognition: The Role of Cerebral Blood Flow.” Nutrients vol. 10,8 986. 27 Jul. 2018, doi:10.3390/nu10080986
- Tran, N et al. “Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) and the Cardiovascular System: in Physiology and in Disease States.” American journal of biomedical science & research vol. 15,2 (2022): 153-177.
- Jackson, Douglas et al. “(-)-Epicatechin Reduces Blood Pressure and Improves Left Ventricular Function and Compliance in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate-Salt Hypertensive Rats.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 23,7 1511. 22 Jun. 2018, doi:10.3390/molecules23071511
- Ramirez-Sanchez, Israel et al. “(-)-Epicatechin improves mitochondrial-related protein levels and ameliorates oxidative stress in dystrophic δ-sarcoglycan null mouse striated muscle.” The FEBS journal vol. 281,24 (2014): 5567-80. doi:10.1111/febs.13098
- Stringer, T P et al. “Plant-derived flavanol (-)epicatechin mitigates anxiety in association with elevated hippocampal monoamine and BDNF levels, but does not influence pattern separation in mice.” Translational psychiatry vol. 5,1 e493. 6 Jan. 2015, doi:10.1038/tp.2014.135
source https://nootropicology.com/epicatechin/