In today's fast-paced world, the demand for cognitive enhancers that can improve focus, alertness, and overall mental performance has grown exponentially. Adrafinil, a wakefulness-promoting agent and nootropic, has gained increasing attention for its potential cognitive benefits.
Initially developed in France, Adrafinil (also known as Olmifon or CRL-40028) is a prodrug for Modafinil (Provigil), another well-known cognitive enhancer. Both substances have been used to combat various sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy.
They have been explored for their potential applications in a wide range of cognitive disorders and conditions requiring enhanced mental performance. This article aims to provide an in-depth overview of Adrafinil, delving into its chemical structure, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, cognitive benefits, safety profile, and legal status.
By examining relevant clinical studies and the latest scientific findings, I aim to comprehensively understand Adrafinil's potential as a cognitive enhancer and its implications for various populations.
So without further ado, let's dive in, shall we?
Overview of Adrafinil as a Nootropic

Adrafinil (CRL-40028) is a synthetic eugeroic, or wakefulness-promoting agent, that was developed by French researchers in the 1970s. It belongs to a class of compounds called nootropics, which are cognitive enhancers often referred to as "smart drugs."
Nootropics are known for their potential to improve various aspects of cognitive function, including memory, attention, and mental processing speed, without causing significant side effects or dependency issues.
Adrafinil is a prodrug for Modafinil, which means that it is converted into Modafinil in the liver through a metabolic process. As a result, Adrafinil shares many of the same pharmacological effects as Modafinil, although with a slower onset of action due to the required metabolic conversion.
The primary advantage of using Adrafinil over Modafinil is its legal status and availability as an over-the-counter supplement (OTC) in many countries, including the United States. Off-label, Adrafinil has been utilized to treat various conditions, including narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of sleep.
It has also been explored as a potential treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a condition marked by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Moreover, Adrafinil has been used to alleviate the symptoms of shift work sleep disorder (SWSD), a circadian rhythm sleep disorder that affects individuals who work during non-traditional hours, leading to difficulties in maintaining alertness and cognitive performance during their work shifts.
In addition to its applications in treating sleep and attention disorders, Adrafinil has gained popularity among students and healthy individuals, in general, seeking to enhance their cognitive performance, especially in situations requiring increased alertness, focus, and mental stamina.
Adrafinil's Chemical Structure and Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Information |
|---|---|
| Trade Names | Olmifon |
| Other Names | CRL-40028 |
| Routes of Administration | Oral |
| ATC Code | N06BX17 (WHO) |
| Formula | C15H15NO3S |
| Molar Mass | 289.35 g·mol−1 |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Metabolism | 75% (liver) |
| Metabolites | Modafinil |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour (T1/2 is 12–15 hours for modafinil) |
| Excretion | Kidney |
Chemical Structure and Properties
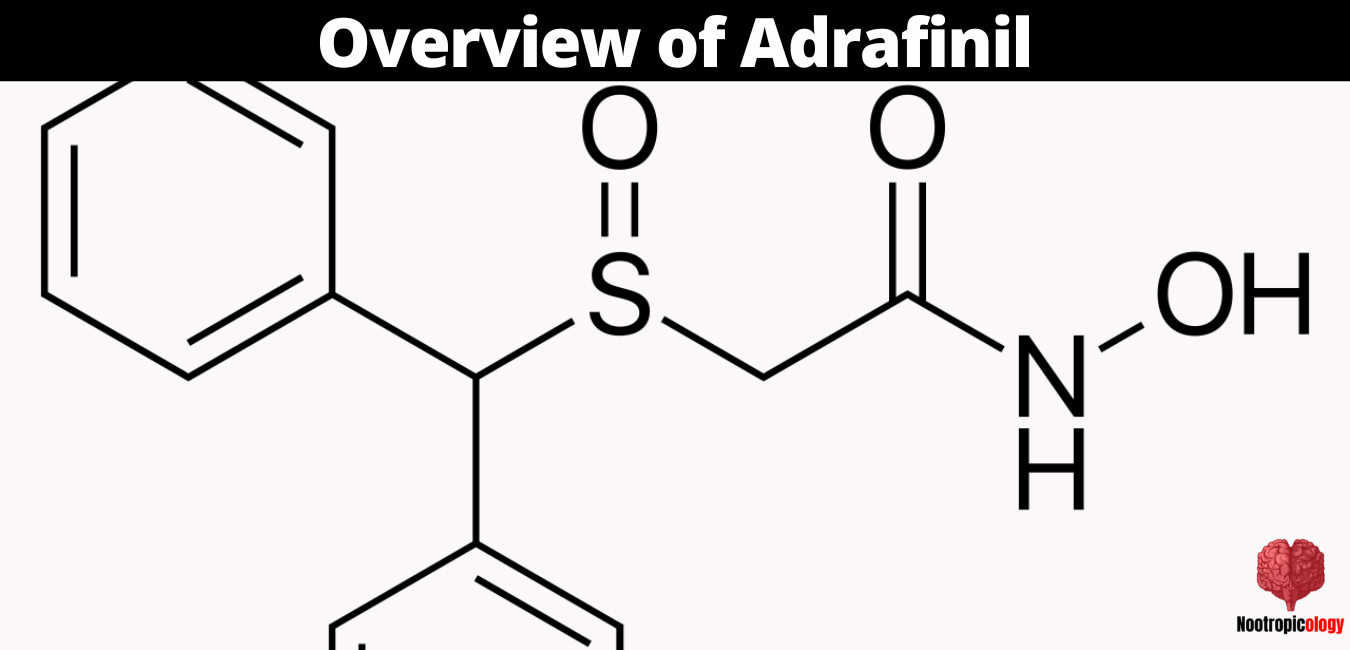
Adrafinil's chemical structure consists of a diphenylmethyl sulfinyl group attached to a hydroxyacetamide group. Its molecular formula is C15H15NO3S, with a molecular weight of 289.35 g/mol.
The compound appears as a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and chloroform. The CAS number for Adrafinil is 63547-13-7, which serves as a unique identifier for the compound in various chemical databases.
Metabolism and Conversion to Modafinil
After oral administration, Adrafinil undergoes hepatic metabolism in the liver, where it is converted into its active metabolite, Modafinil. This biotransformation process involves two primary enzymatic reactions:
- The reduction of the sulfoxide group to a sulfide group.
- The hydrolysis of the amide bond.
These reactions form the pharmacologically active compound Modafinil and its inactive byproduct, modafinilic acid. The conversion to Modafinil is critical for Adrafinil's cognitive-enhancing effects, as it is Modafinil that exerts the majority of the pharmacological actions in the body.[1]
Pharmacokinetics, Half-life, and Bioavailability
Adrafinil exhibits a relatively short half-life of about 1 hour in humans. However, it should be noted that the half-life of its active metabolite, Modafinil, is considerably longer at 12-15 hours. The bioavailability of Adrafinil ranges from 50% to 80%, which means that a significant portion of the orally administered drug reaches systemic circulation and is available to exert its effects.
The absorption of Adrafinil is slow and gradual, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 1-2 hours following oral administration. This slow absorption rate contributes to the delayed onset of action when compared to Modafinil.
Adrafinil is distributed throughout the body after it is absorbed, with a stronger preference for the central nervous system (CNS), where it improves cognitive function. The kidneys get rid of the drug, primarily through urinary excretion of its metabolites, which include modafinilic acid and other minor metabolites.
The elimination of Adrafinil and its metabolites is essential for preventing drug accumulation and potential adverse effects associated with prolonged use.
Adrafinil's Mechanism of Action (MOA)
To better understand the effects of Adrafinil, it is essential to delve into its mechanism of action. Adrafinil primarily works by modulating the activity of specific neurotransmitters in the brain, affecting a range of systems that contribute to its cognitive-enhancing properties.
The primary systems influenced by Adrafinil include:
Orexinergic System
Adrafinil stimulates the release of orexin, a neuropeptide that plays a crucial role in promoting wakefulness, arousal, and vigilance. This action is achieved by activating orexin-producing neurons in the hypothalamus. As orexin levels increase, the brain's overall state of alertness and wakefulness is enhanced, leading to improved cognitive performance.[2]
Histaminergic System
Adrafinil indirectly influences the histaminergic system by increasing orexinergic activity. This interaction results in the stimulation of histamine release, a neurotransmitter involved in regulating wakefulness and arousal. The increased histamine release leads to enhanced firing of histaminergic neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus, further promoting wakefulness and attention.[3]
Adrenergic System
Adrafinil impacts the adrenergic system by boosting the release of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter associated with alertness, focus, and concentration. This enhancement occurs through the inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake and the activation of α1-adrenergic receptors, leading to increased availability of norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft and greater stimulation of its target receptors.[4]
Dopaminergic System
Adrafinil exerts a moderate influence on the dopaminergic system by inhibiting dopamine reuptake and promoting dopamine release. This modulation of dopamine levels contributes to improved attention, motivation, and reward-related processes, which are essential for goal-directed behavior and cognitive performance.[5]
Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems
Adrafinil also plays a role in modulating the activity of the glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmitter systems. By influencing glutamate and GABA neurotransmission, Adrafinil helps establish a balanced excitation-inhibition relationship in the brain, which is critical for optimal cognitive function.
This modulation enhances learning, memory, and overall cognitive performance by fine-tuning the intricate balance between excitatory and inhibitory signaling in the brain.[6]
Cognitive Benefits of Adrafinil (Clinical Studies and Efficacy)

Now that we know the exact mechanisms behind how Adrafinil works, let's explore how it can benefit you and what that means for your cognitive performance. But before I dive into the scientific literature, it's worth pointing out that the majority of the science has been done on the related compounds Modafinil and Armodafinil.
That said, and since Adrafinil is a prodrug of Modafinil, it is reasonable to assume that these two compounds would have similar effects. In fact, several studies suggest this to be the case.
Alertness and Wakefulness
Adrafinil's stimulatory effects on the central nervous system have been shown to counteract fatigue and drowsiness in sleep-deprived individuals. Adrafinil enhances arousal and alertness by increasing the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, mitigating the cognitive impairments typically associated with sleep deprivation.[7]
Effects on Shift Work Sleep Disorder (SWSD)
Adrafinil has demonstrated efficacy in managing shift work sleep disorder, a condition characterized by excessive sleepiness and difficulty maintaining alertness during nighttime work hours. Its capacity to promote wakefulness and improve cognitive function enables individuals to better adapt to atypical work schedules.[8]
Attention and Focus
Adrafinil's influence on catecholaminergic systems modulates attentional processes, promoting sustained attention and focus. Its ability to enhance vigilance and cognitive control can improve task performance in various domains, including academic and occupational settings.[9]
Influence on Attentional Processes
Research has identified Adrafinil's impact on prefrontal cortex activity as a key factor in improving attentional processes. By increasing neuronal firing rates and modulating the release of neurotransmitters, Adrafinil facilitates the efficient allocation of cognitive resources and enables heightened focus.[10]
Improvement in Task Performance
Adrafinil's nootropic effects have been linked to enhanced task performance, particularly in tasks requiring sustained attention, working memory, and executive function. Its impact on neural activation and neurotransmitter release contributes to improved cognitive flexibility, enabling users to excel in complex, demanding tasks.
Effects on Working Memory
Adrafinil has demonstrated the capacity to improve working memory performance by modulating dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission. Its influence on prefrontal cortex activation and neural connectivity contributes to more efficient processing and storage of information in short-term memory.
Long-term Potentiation
Adrafinil facilitates long-term potentiation (LTP), a critical process underlying memory formation and consolidation.[11] Adrafinil can enhance synaptic plasticity by modulating glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmission, promoting the strengthening of neuronal connections and the formation of long-term memories.
Potential Antidepressant Effects
Adrafinil's ability to modulate monoaminergic systems has been associated with potential antidepressant properties. By increasing dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin levels, adrafinil may alleviate depressive symptoms and improve overall mood regulation.
Anxiolytic Properties
Though not as extensively researched in humans, some animal studies suggest Modafinil and Adrafinil possess anxiolytic properties, potentially reducing anxiety levels and promoting emotional stability. Its influence on neurotransmitter systems and neural circuitry involved in emotion regulation may contribute to these effects.[12]
Adrafinil Safety and Side Effects

Although Adrafinil is generally considered a safe and well-tolerated substance, some potential side effects are still associated with its use. Let's look at some of the most common ones below.
Common Adrafinil Adverse Effects
Adrafinil administration has been associated with several common side effects, including headache, dizziness, nausea, and insomnia. These adverse effects are generally mild in nature and tend to resolve spontaneously without medical intervention.
However, if these side effects persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Liver Enzyme Elevation
The metabolic conversion of Adrafinil to its active metabolite, Modafinil, occurs predominantly in the liver. In some cases, Adrafinil has been linked to elevated liver enzymes, possibly due to increased hepatic stress resulting from its biotransformation.
As a precautionary measure, individuals using Adrafinil, particularly during long-term use, should monitor liver function through periodic blood tests to ensure optimal hepatic health.
Drug Interactions
Adrafinil may interact with various medications as a psychoactive substance, leading to altered pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics.
Examples of medications that may interact with Adrafinil include:
- Anticoagulants, which could exacerbate bleeding risks
- Anticonvulsants, potentially resulting in reduced seizure control
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which may increase the risk of serotonergic toxicity.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before combining Adrafinil with other medications to minimize the risk of adverse drug interactions.
Contraindications and Precautions
Certain populations should exercise caution when considering adrafinil use or avoid it altogether. Individuals with a history of liver disease, cardiovascular disease, or severe hypertension should refrain from using adrafinil, as it may exacerbate existing health conditions.
Additionally, pregnant or breastfeeding women should exercise caution, as the safety of adrafinil in these populations has not been well-established.
Individuals with a history of psychiatric disorders should consult a healthcare professional before using adrafinil, as it may potentially trigger or exacerbate psychiatric symptoms.
Adrafinil Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of Adrafinil varies depending on individual factors but typically ranges from 150 to 300 mg per day, administered orally.
To minimize the risk of adverse effects and to gauge individual response, it is advisable to initiate therapy at a lower dose and gradually titrate the dosage upwards as needed.
Adrafinil has a relatively long half-life, so it should ideally be taken in the morning or early afternoon to minimize the risk of sleep disturbances.
Legal and Regulatory Status of Adrafinil
As previously mentioned, Adrafinil is an over-the-counter (OTC) drug in the United States and European Union. However, its legal status varies between countries, as do the specific regulations governing its use.
Here is a more detailed overview of Adrafinil's legal and regulatory status in various regions:
- Adrafinil in the United States: In the United States, Adrafinil is not FDA-approved for any medical indication. However, it is available as an unscheduled, over-the-counter dietary supplement. The US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) does not classify Adrafinil as a controlled substance, which means that buying, possessing, and using Adrafinil without a prescription is legal. That being said, individual state regulations may vary, and it is essential to be aware of local laws.
- Adrafinil in Europe and other countries: In Europe, Adrafinil has been discontinued and is no longer available for prescription. However, its legal status varies by country, with some countries classifying it as a prescription medication and others as a controlled substance with restrictions on its use and distribution.
- United Kingdom: Adrafinil is a prescription-only medication (POM) in the UK. Possessing and using Adrafinil with a valid prescription is legal, but it is illegal to supply or import without a proper license.
- France: Adrafinil was initially developed in France, but its sale has been discontinued. The possession and use of Adrafinil are not regulated, but selling or distributing the substance requires a pharmaceutical license.
- Germany: In Germany, Adrafinil is considered a prescription medication. Possessing and using Adrafinil without a prescription is illegal, and unauthorized sale or distribution is strictly prohibited.
- Canada: Adrafinil is not regulated under Canada's Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, and its possession is legal. However, it is not approved for sale by Health Canada, and importing the substance for personal use is subject to restrictions.
- Australia: Adrafinil is classified as a Schedule 4 (Prescription Only) substance in Australia. Possession and use of Adrafinil require a valid prescription, and unauthorized sale or distribution is prohibited.
Given the variations in legal status and regulations across different countries, it is essential to research and adhere to the specific laws and regulations governing Adrafinil's use in your jurisdiction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Let's look at the most frequently asked about Adrafinil.
Where Can I Buy Adrafinil?
Adrafinil can be purchased online through various reputable vendors, such as Science.bio, which is based in the United States and ships worldwide. When buying Adrafinil, selecting a vendor that ensures the purity and quality of the product is crucial. Look for vendors that provide third-party lab testing results or certificates of analysis to verify the product's authenticity and potency.
How Long Does It Take for Adrafinil to Kick In?
The onset of Adrafinil's effects is variable and depends on factors such as individual metabolism, dosage, and the presence of food in the stomach. Generally, Adrafinil's effects begin to manifest within 1-2 hours after oral ingestion. However, some individuals may experience a faster onset of action, while others may take longer to feel the effects.
What Does Adrafinil Feel Like?
The subjective experience of Adrafinil varies between individuals, but generally, users report feeling increased alertness, wakefulness, and mental clarity. Unlike traditional stimulants like amphetamines or caffeine, Adrafinil's effects are typically described as smoother and more subtle, without the jitteriness or excessive agitation commonly associated with other stimulants.
Can I Stack Adrafinil With Other Medications or Nootropic Supplements?
Adrafinil can interact with certain medications or nootropic supplements, leading to altered pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before combining Adrafinil with other medications, particularly anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Additionally, be cautious when combining Adrafinil with other stimulants or supplements that affect the central nervous system, as this can lead to overstimulation.
Is Adrafinil Addictive?
Adrafinil is not considered to be highly addictive; however, it is possible to develop a psychological dependence on its stimulating and cognitive-enhancing effects. While the risk of addiction is relatively low compared to traditional stimulants like amphetamines, it is essential to use Adrafinil responsibly and follow the recommended dosage guidelines. To minimize the risk of dependence, consider cycling Adrafinil use, taking periodic breaks to allow your body and brain to return to their baseline states.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects of Adrafinil Use?
While some users experience cognitive benefits with sustained use, it is essential to be cautious when using Adrafinil long-term, as the potential risks and side effects are not yet fully known. One potential concern with long-term use is the potential for liver enzyme elevation due to Adrafinil's hepatic metabolism. Monitoring liver function during extended use is recommended to minimize potential risks.
Can I Take Adrafinil Every Day?
Although some users may take Adrafinil daily, it is generally recommended to use it on an as-needed basis or to cycle its use, taking breaks to prevent tolerance or dependence. Using Adrafinil daily may increase the risk of side effects or adverse reactions, particularly if used at high doses or in combination with other stimulants or medications.
Conclusion
Adrafinil, a potent smart drug, has shown significant cognitive-enhancing effects, including increased alertness, energy, wakefulness, attention, memory, and mood regulation. These benefits stem from its ability to modulate various neurotransmitter systems, such as the orexinergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, dopaminergic, and glutamatergic systems.
Products containing Adrafinil have demonstrated their potential in helping patients with conditions like narcolepsy, ADHD, and SWSD, as well as healthy individuals seeking cognitive improvement.
Clinical trials and patient reports indicate that Adrafinil has potential applications in a wide range of populations. Furthermore, the development of agonists and agents targeting similar pathways in pharmacology is underway, which may lead to even more effective cognitive enhancers.
However, it is crucial to continue researching Adrafinil to better understand its mechanisms of action, long-term safety, and possible applications in an even broader array of cognitive disorders. This ongoing investigation will be instrumental in the development of more effective and safer cognitive enhancers in the future.
As the body of knowledge surrounding Adrafinil grows, resources like PubMed, Wikipedia, and similar references and lists will be invaluable for staying up-to-date with the latest findings.
It is important to consider the ethical implications of using such cognitive enhancers in vivo, particularly in animal models like rats, and to conduct responsible research that advances our understanding of these substances.
- Dubey, S et al. “A novel study of screening and confirmation of modafinil, adrafinil and their metabolite modafinilic acid under EI-GC-MS and ESI-LC-MS-MS ionization.” Indian journal of pharmacology vol. 41,6 (2009): 278-83. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.59928
- Salerno, Monica et al. “Modafinil and orexin system: interactions and medico-legal considerations.” Frontiers in bioscience (Landmark edition) vol. 24,3 564-575. 1 Jan. 2019, doi:10.2741/4736
- Ishizuka, Tomoko et al. “Modanifil activates the histaminergic system through the orexinergic neurons.” Neuroscience letters vol. 483,3 (2010): 193-6. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.005
- Milgram, N W et al. “Oral administration of adrafinil improves discrimination learning in aged beagle dogs.” Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior vol. 66,2 (2000): 301-5. doi:10.1016/s0091-3057(00)00175-1
- Gerrard, Paul, and Robert Malcolm. “Mechanisms of modafinil: A review of current research.” Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment vol. 3,3 (2007): 349-64.
- Ferraro, L et al. “The antinarcoleptic drug modafinil increases glutamate release in thalamic areas and hippocampus.” Neuroreport vol. 8,13 (1997): 2883-7. doi:10.1097/00001756-199709080-00016
- Wesensten, Nancy J. “Effects of modafinil on cognitive performance and alertness during sleep deprivation.” Current pharmaceutical design vol. 12,20 (2006): 2457-71. doi:10.2174/138161206777698819
- Gude, Dilip. “Waking up to modafinil in shift work sleep disorder.” Industrial psychiatry journal vol. 20,2 (2011): 145. doi:10.4103/0972-6748.102533
- Wisor, Jonathan. “Modafinil as a catecholaminergic agent: empirical evidence and unanswered questions.” Frontiers in neurology vol. 4 139. 7 Oct. 2013, doi:10.3389/fneur.2013.00139
- Minzenberg, M., Carter, C. "Modafinil: A Review of Neurochemical Actions and Effects on Cognition." Neuropsychopharmacol33, 1477–1502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301534
- Yan, Wen-Wen et al. “Effects of Modafinil on Behavioral Learning and Hippocampal Synaptic Transmission in Rats.” International neurourology journal vol. 19,4 (2015): 220-7. doi:10.5213/inj.2015.19.4.220
- Johnson, Adrian, and Trevor James Hamilton. “Modafinil decreases anxiety-like behaviour in zebrafish.” PeerJ vol. 5 e2994. 14 Feb. 2017, doi:10.7717/peerj.2994
source https://nootropicology.com/adrafinil/

No comments:
Post a Comment