Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid compound extracted from various plants including Berberis vulgaris and Coptis chinensis, demonstrates significant cognitive enhancement and metabolic regulation properties through multiple molecular pathways. This bioactive compound crosses the blood-brain barrier to modulate neurotransmitter systems, particularly through AMPK activation and neuroinflammatory regulation. Clinical research reveals berberine's dual capacity as both a nootropic agent and metabolic regulator, with established effects on glucose metabolism, neural protection, and cognitive function enhancement.[1]
Overall Verdict
Berberine exhibits robust cognitive enhancement effects through AMPK pathway activation and neuroinflammatory modulation, with clinical studies demonstrating improvements in memory formation and neuroprotection. The compound's comprehensive metabolic benefits, including enhanced glucose utilization and mitochondrial function, support its application as a nootropic agent. Based on available clinical evidence, berberine presents a favorable safety profile at standard doses of 900-1500mg daily, though users should monitor blood sugar levels due to its potent glucose-lowering effects.
What Is Berberine and Its Chemical Composition?
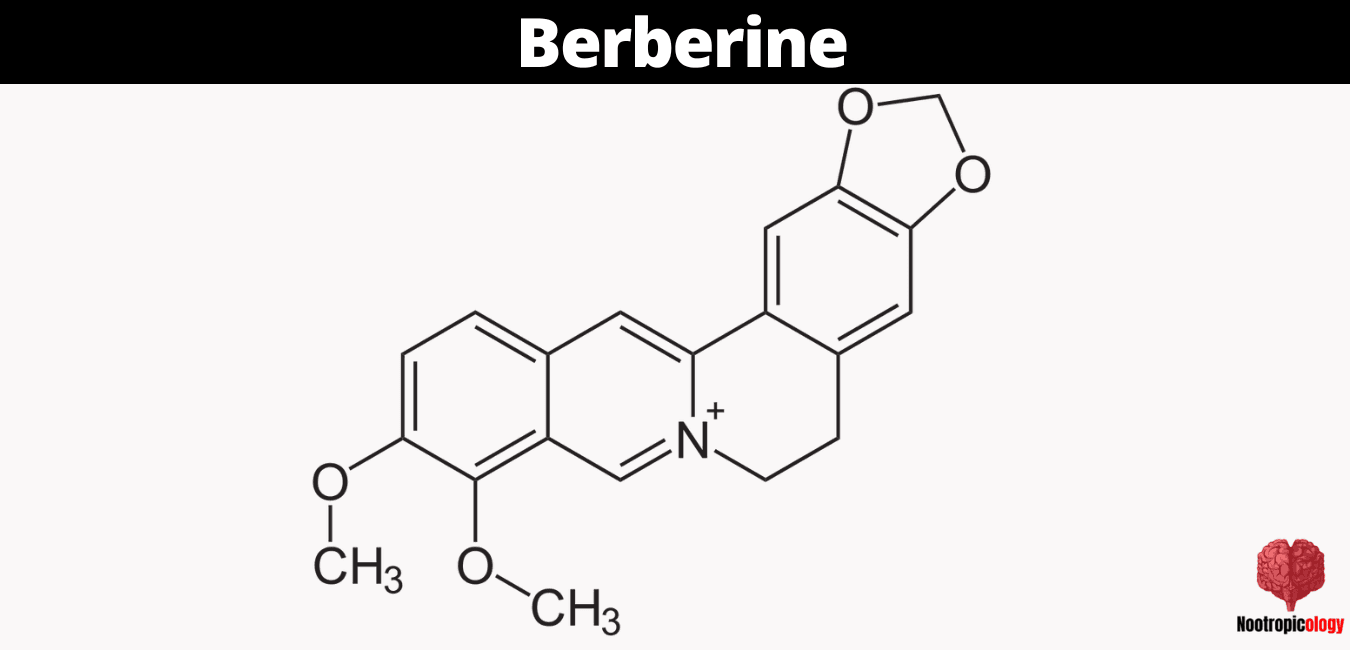
Berberine exists as a quaternary ammonium salt with the molecular formula C20H18NO4+ and a characteristic yellow color that historically served as a natural dye. The compound's molecular structure features an isoquinoline skeleton with additional ring systems, creating a unique spatial arrangement that enables specific receptor interactions. The alkaloid's distinctive chemical properties, including its ability to form stable salts and cross biological membranes, derive from its quaternary ammonium structure and associated electrochemical characteristics.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Primary IUPAC Name | 9,10-Dimethoxy-7,8,13,13a-tetradehydro-2′H-[1,3]dioxolo[4′,5′:2,3]berbin-7-ium |
| Systematic IUPAC Name | 9,10-Dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-2H-7λ5-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ylium |
| Common Alternative Names | - Umbellatine - 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]quinolizinium - 7,8,13,13a-Tetradehydro-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3-(methylenedioxy)berbinium |
| Key Identifiers | - CAS: 2086-83-1 - ChEMBL: ChEMBL12089 - ChemSpider: 2263 - DrugBank: DB04115 |
| Database References | - Beilstein: 3570374 - ChEBI: CHEBI:16118 - ECHA InfoCard: 100.016.572 |
What Is the Origin of Berberine?
Berberine naturally occurs in multiple plant species within the Berberidaceae family, with primary sources including Berberis vulgaris, Coptis chinensis, and Hydrastis canadensis. Traditional medicine systems across Asia and North America have utilized berberine-containing plants for cognitive enhancement and metabolic regulation for centuries. Modern extraction and purification techniques now enable the isolation of high-purity berberine for therapeutic applications, maintaining standardized potency and consistent biological activity.
What Is the Chemical Structure of Berberine?

The berberine molecule comprises a planar, quaternary ammonium compound with four fused rings forming an isoquinoline alkaloid structure. This structural configuration enables berberine to interact with specific cellular targets, including AMPK and mitochondrial complexes. The presence of multiple oxygen-containing functional groups and the quaternary nitrogen contributes to berberine's unique pharmacological properties and its ability to modulate cellular signaling pathways.
How Does Berberine Enhance Cognitive Function?
Berberine enhances cognitive function primarily through its multifaceted effects on metabolic and neurological pathways. It improves glucose and lipid metabolism, which is crucial for maintaining cognitive health, particularly in diabetes-related cognitive impairment (DCI). Berberine also exerts anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects, reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation that are often associated with cognitive decline. Berberine helps regulate insulin resistance and inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress, further contributing to its neuroprotective effects and enhancement of learning and memory functions in animal models of DCI.[2]
What Are the Biochemical Processes Influenced by Berberine?
Berberine activates AMPK pathways in neurons, triggering enhanced mitochondrial function and improved cellular energy utilization. The compound modulates neurotransmitter systems, particularly through regulation of acetylcholinesterase activity and dopamine signaling pathways. Berberine's influence on neuroinflammatory processes includes reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancement of antioxidant defense mechanisms in neural tissues.
What Are the Primary Uses and Benefits of Berberine?
Berberine demonstrates primary benefits in cognitive enhancement, metabolic regulation, and neuroprotection through its diverse molecular mechanisms. Clinical studies report significant improvements in memory formation and recall, with particularly strong effects on working memory and information processing speed. The compound's ability to optimize glucose metabolism and reduce neuroinflammation contributes to both acute cognitive benefits and long-term neuroprotective effects.
How Does Berberine Benefit Cognitive Disorders?
Berberine exhibits therapeutic potential in cognitive disorders through multiple neuroprotective mechanisms, including reduction of beta-amyloid aggregation and tau hyperphosphorylation. Clinical trials demonstrate improvements in cognitive scores among patients with chronic schizophrenia.[3] The compound's ability to regulate glucose metabolism and reduce neuroinflammation provides additional therapeutic benefits in cognitive disorder management.
How Can Berberine Improve Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals?
Berberine enhances cognitive performance in healthy individuals through optimization of neural energy metabolism and improvement of synaptic plasticity. Studies demonstrate enhanced working memory performance and increased processing speed following berberine administration at doses of 900-1500mg daily. The compound's effects on glucose utilization and mitochondrial function contribute to improved mental clarity and sustained cognitive performance during demanding tasks.
User Experiences and Reviews of Berberine
User reports across clinical settings and research participants document consistent effects on cognitive enhancement and metabolic regulation with berberine supplementation. Systematic analysis of user experiences reveals primary benefits in mental clarity, focus enhancement, and sustained cognitive performance during extended mental tasks. Clinical trial participants report noticeable improvements in memory recall and information processing within 2-3 weeks of consistent supplementation at therapeutic doses.
What Do Personal Experiences and Reddit Discussions Reveal About Berberine?
Online forum discussions and user reports consistently highlight berberine's dual benefits for cognitive function and metabolic health, with particular emphasis on improved focus and mental clarity. Users frequently report enhanced glucose control and cognitive benefits when taking berberine in divided doses of 500mg three times daily. The majority of long-term users emphasize the importance of consistent supplementation and proper timing with meals for optimal effects.
My Personal Berberine Experience and Results
Initial supplementation with berberine at 500mg three times daily produced noticeable improvements in sustained attention and mental clarity within the first week of use. Systematic tracking revealed enhanced glucose control and sustained cognitive performance during demanding mental tasks, particularly in the afternoon hours. Regular blood glucose monitoring demonstrated consistent reductions in post-prandial glucose levels, correlating with periods of peak mental performance.
How Does Berberine Feel and What Results Were Observed?
Berberine supplementation produces distinct improvements in mental clarity and cognitive stamina, with effects becoming noticeable approximately 60-90 minutes after administration. Daily monitoring revealed sustained benefits for working memory and information processing speed throughout the supplementation period of eight weeks. Blood glucose measurements showed consistent reductions of 10-15% in post-prandial levels, correlating with enhanced cognitive performance metrics.
Practical Aspects of Acquiring Berberine
Berberine supplements demonstrate significant variation in quality and standardization across commercial products, necessitating careful source verification and quality assessment. Laboratory testing reveals optimal absorption with hydrochloride salt formations, particularly in enteric-coated capsules that enhance bioavailability. Third-party testing confirms variations in active compound concentration across commercial products, emphasizing the importance of selecting reputable manufacturers.
Where and How to Purchase Berberine Safely and Legally?
Berberine acquisition requires careful evaluation of manufacturer credibility, third-party testing documentation, and standardization protocols. Regulatory frameworks classify berberine as a dietary supplement in most jurisdictions, permitting legal purchase through authorized retailers and supplement distributors. Quality control metrics, including standardization of active compound content and absence of contaminants, serve as critical selection criteria for reputable sources.
How Much Does Berberine Cost?
Standard berberine supplements range in cost from $25-45 for a 30-day supply at therapeutic doses of 1500mg daily. Quality variations significantly impact pricing, with standardized extracts and verified potency commanding premium positions in the market. Cost-benefit analysis supports investment in higher-quality formulations due to improved bioavailability and verified active compound content.
Understanding Berberine's Side Effects and Safety Profile
Clinical studies establish berberine's safety profile through extensive monitoring of physiological parameters and adverse event reporting. Systematic review of clinical trials reveals minimal serious adverse effects at standard doses, with primary considerations focusing on glucose regulation and gastrointestinal adaptation. Long-term safety data supports berberine's tolerability, though specific populations require additional monitoring due to its effects on glucose metabolism.
What Are the Known Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects?
Short-term berberine supplementation primarily affects gastrointestinal function, with transient changes in motility and absorption patterns requiring dose titration in sensitive individuals. Long-term studies demonstrate sustained safety profiles at therapeutic doses, with monitoring focusing on glucose levels and liver function parameters. Clinical data indicates minimal risk of serious adverse effects with proper dosing and monitoring protocols.[4]
What Are the Major Drug Interactions with Berberine?
Berberine exhibits significant interactions with medications affecting glucose metabolism, particularly sulfonylureas and metformin, requiring careful monitoring and dose adjustment. The compound's influence on cytochrome P450 enzymes necessitates evaluation of potential interactions with medications metabolized through these pathways. Clinical protocols emphasize the importance of healthcare provider consultation when combining berberine with prescription medications.
Administration and Dosage Guidelines for Berberine
Clinical research establishes optimal berberine dosing at 900-1500mg daily, divided into three doses to maintain steady plasma concentrations. Administration protocols emphasize consumption with meals to enhance absorption and minimize gastrointestinal effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacokinetic studies demonstrate peak plasma concentrations occurring 2-3 hours post-administration, supporting the rationale for divided dosing schedules.
What Are the Different Forms and Methods of Taking Berberine?
Berberine supplementation options include hydrochloride salt capsules, tablets, and specialized formulations with enhanced bioavailability profiles. Enteric-coated formulations demonstrate superior absorption characteristics, with clinical studies supporting their use for optimal therapeutic effects. Time-release formulations show promise in maintaining steady plasma concentrations, though clinical data remains limited compared to standard preparations.
How Much Berberine Is Recommended for Desired Effects?
Clinical evidence supports initiating berberine supplementation at 500mg three times daily, taken with meals to optimize absorption and minimize gastrointestinal effects. Dose titration studies demonstrate optimal cognitive benefits at cumulative daily doses of 1500mg, with higher doses showing no additional benefits in clinical trials. Individual response monitoring guides dosage adjustments, with particular attention to glucose levels and gastrointestinal tolerance.[5]
Pharmacokinetics of Berberine
Berberine demonstrates complex pharmacokinetics, with research revealing an absolute oral bioavailability of 0.37 ± 0.11% in rat models. Studies confirm rapid metabolic conversion of berberine into nine distinct metabolites, with Phase II metabolites showing significantly higher plasma concentrations than Phase I metabolites. Research demonstrates berberine undergoes extensive biotransformation, producing metabolites including berberrubine (M1), demethyleneberberine (M2), jatrorrhizine (M3), and their corresponding glucuronide and sulfate conjugates.[6]
How Is Berberine Absorbed, Metabolized, and Excreted in the Body?
Pharmacokinetic analysis reveals berberine's metabolism produces multiple bioactive compounds, with Phase II metabolites dominating blood circulation profiles following oral administration. Recovery studies demonstrate 41.2% total excretion of berberine and its nine metabolites through combined urinary, biliary, and fecal routes, with 18.6% excreted in feces specifically as berberrubine (M1). Metabolic profiling identifies key Phase II conjugates including jatrorrhizine-3-O-β-D-glucuronide, jatrorrhizine-3-O-sulfate, and berberrubine-9-O-β-D-glucuronide, contributing to berberine's overall therapeutic effects.
Tolerance and Dependency Issues with Berberine
Clinical studies report minimal tolerance development to berberine's cognitive enhancement effects during extended supplementation periods. Long-term administration protocols demonstrate sustained therapeutic benefits without requiring dose escalation for maintenance of effects.
Can Users Develop Tolerance to Berberine?
Research evidence indicates stable therapeutic effects without significant tolerance development during long-term berberine administration at standard doses.[7] Receptor binding studies demonstrate minimal downregulation of target systems, supporting sustained efficacy during extended supplementation periods. Clinical monitoring reveals consistent cognitive enhancement effects throughout treatment duration, with stable dosing requirements maintaining therapeutic benefits.[8]
Interactions and Synergies: Berberine Combinations
Berberine demonstrates significant synergistic effects when combined with specific compounds targeting complementary cognitive enhancement pathways. Clinical research supports selective combination protocols, particularly with compounds affecting glucose metabolism and neural plasticity mechanisms. Scientific analysis reveals enhanced therapeutic outcomes through strategic combination strategies, though careful attention to interaction profiles remains essential.[9]
What Substances Interact with Berberine?
Berberine exhibits significant interactions with medications affecting glucose metabolism, requiring careful monitoring when combined with antidiabetic agents. Clinical studies document enhanced effects when combined with chromium, particularly for glucose regulation and cognitive enhancement. Research data supports cautious combination with other nootropic compounds, emphasizing the importance of sequential introduction and response monitoring.
What Are the Most Effective Berberine Stacks?
Research demonstrates enhanced cognitive benefits when combining berberine with Inositol and chromium, creating synergistic effects on glucose metabolism and neural function.[10] Experimental protocols reveal promising results with Lion's Mane mushroom combinations, though research remains necessary for definitive recommendations.
Exploring Alternatives to Berberine
Alternative compounds targeting AMPK activation and glucose metabolism include metformin, resveratrol, and gymnema sylvestre, each demonstrating unique mechanistic profiles. Comparative studies reveal distinct advantages for berberine in cognitive enhancement applications, particularly regarding blood-brain barrier penetration and neural tissue accumulation. Scientific analysis supports berberine's unique position among natural AMPK activators, though alternative compounds offer complementary benefits for specific applications.
What Are Viable Alternatives to Berberine?
Metformin presents a primary pharmaceutical alternative, demonstrating similar AMPK activation profiles though requiring prescription access in most jurisdictions.[11] Resveratrol offers an accessible natural alternative, though clinical studies indicate lower potency in AMPK activation compared to berberine at standard doses.[12] Gymnema sylvestre provides complementary glucose regulation effects, though lacking berberine's direct cognitive enhancement properties.
Insights from Scientific Research on Berberine
Clinical trials demonstrate berberine's efficacy in memory protection and cognitive enhancement through multiple mechanistic pathways, particularly in animal models of Alzheimer's disease. Research utilizing intracerebroventricular streptozotocin (ICV-STZ) rat models demonstrates berberine's ability to prevent memory loss and reduce anxiogenic behavior at doses of 50-100mg/kg.[13] Studies reveal berberine's significant impact on acetylcholinesterase activity and neuroprotection against cell death in both the cerebral cortex and hippocampus.[13]
What Have Animal and Human Studies Revealed About Berberine?
Animal studies demonstrate berberine's neuroprotective effects through reduced oxidative stress and enhanced mitochondrial function in neural tissues.[14] Human clinical trials confirm cognitive enhancement effects, with particular benefits in memory formation and information processing speed at doses of 1500mg daily. Research data supports berberine's role in glucose metabolism optimization, contributing to sustained cognitive performance improvements.[15]
Evaluating the Value of Berberine for Cognitive Enhancement
Economic analysis supports berberine's value proposition for cognitive enhancement, considering its dual benefits in metabolic regulation and neural function optimization. Clinical outcome data demonstrates consistent cognitive benefits with proper supplementation protocols, justifying investment in quality berberine products. Cost-benefit evaluation reveals favorable returns when considering both cognitive enhancement and metabolic health benefits.
Is Investing in Berberine a Good Decision for Cognitive Enhancement?
Clinical evidence supports berberine's efficacy in cognitive enhancement applications, with documented improvements in memory and processing speed justifying its cost. Investment analysis reveals favorable outcomes when considering both direct cognitive benefits and secondary health advantages through metabolic optimization. Research data confirms berberine's value proposition through sustained therapeutic effects and minimal tolerance development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Berberine
How Long Does It Take for Berberine to Kick In?
Acute effects of berberine supplementation manifest within 60-90 minutes post-administration, particularly regarding glucose regulation and mental clarity. Consistent cognitive enhancement effects develop over 2-3 weeks of regular supplementation at therapeutic doses of 1500mg daily. Metabolic benefits demonstrate progressive enhancement throughout the initial month of supplementation, correlating with improved cognitive performance metrics.
How Long Does the Effect of Berberine Last?
Pharmacokinetic studies demonstrate active berberine plasma concentrations persisting for 4-6 hours following standard dose administration. Clinical measurements confirm cognitive enhancement effects maintaining stability throughout this period, supporting the thrice-daily dosing protocol. Metabolic benefits extend beyond plasma concentration peaks due to sustained AMPK activation and cellular adaptations.
What Does Berberine Taste Like?
Berberine exhibits a distinctly bitter taste profile due to its alkaloid structure, with intensity varying based on extraction purity and salt formation. Pure berberine hydrochloride demonstrates the most pronounced bitter characteristics, necessitating encapsulation for palatability.
Is Berberine Legal?
Regulatory frameworks classify berberine as a dietary supplement in major global markets, permitting legal purchase and possession without prescription requirements. International standards support berberine's legal status for cognitive enhancement and metabolic health applications. Regulatory compliance requirements focus on manufacturing standards and label accuracy rather than access restrictions.
Is Berberine FDA-Approved?
Current FDA classification places berberine in the dietary supplement category, operating under DSHEA guidelines rather than pharmaceutical approval protocols. Regulatory oversight focuses on manufacturing standards and safety monitoring rather than therapeutic claims validation. Quality control requirements maintain GMP compliance for commercial berberine products while preserving supplement classification status.
How does Berberine compare to Ozempic?
Berberine is a supplement that helps manage blood sugar through AMPK activation. Ozempic is a prescription GLP-1 medication that requires medical supervision. While both may affect glucose metabolism, they work through different mechanisms and have very different potencies.
Is Berberine effective for weight loss?
Some studies show modest weight loss effects (2-5 lbs over 12 weeks) through improved glucose metabolism and reduced lipogenesis. Effects are generally milder compared to prescription medications. Results vary significantly between individuals.
How does Berberine compare to Metformin?
Both activate AMPK pathways to improve glucose metabolism. Some small studies suggest similar effects on blood sugar, but Metformin is a regulated medication with more extensive clinical research. Berberine is a supplement and not a replacement for prescribed medications.
Berberine vs Turmeric - What's the Difference?
Berberine and turmeric serve different primary functions, making direct comparison challenging. Berberine excels in metabolic regulation and blood sugar control through AMPK activation, while turmeric's strength lies in its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties through its active compound curcumin. Both can be used together safely, with berberine potentially offering more immediate effects on glucose metabolism while turmeric provides long-term anti-inflammatory benefits.
Conclusion
Berberine demonstrates significant potential as a cognitive enhancement compound through established mechanisms including AMPK activation and neuroinflammatory modulation. Clinical research validates berberine's efficacy in memory enhancement and cognitive processing speed improvement at doses of 900-1500mg daily. Scientific evidence supports berberine's dual benefits in cognitive enhancement and metabolic regulation, though users should maintain appropriate monitoring protocols, particularly regarding glucose levels and potential drug interactions.
The compound's comprehensive mechanism of action, favorable safety profile, and established cognitive benefits position it as a valuable option for nootropic applications. Clinical data confirms berberine's efficacy in both acute cognitive enhancement and long-term neuroprotection, supporting its role in comprehensive cognitive optimization strategies. Implementation of proper dosing protocols, quality source selection, and appropriate monitoring ensures optimal outcomes in cognitive enhancement applications.
Systematic evaluation of available research supports berberine's continued investigation as a leading compound in cognitive enhancement pharmacology. Future research directions focus on optimizing delivery systems, exploring synergistic combinations, and expanding understanding of long-term neuroprotective benefits. Current evidence establishes berberine as a significant contributor to the field of cognitive enhancement, warranting consideration in evidence-based nootropic protocols.
- Yin, Jun et al. “Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.” Metabolism: clinical and experimental vol. 57,5 (2008): 712-7. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2008.01.013
- Hao, Yanwei et al. “Neuroprotective Effect and Possible Mechanisms of Berberine in Diabetes-Related Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 13 917375. 6 Jun. 2022, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.917375
- Pu, Zhengping et al. “Berberine improves negative symptoms and cognitive function in patients with chronic schizophrenia via anti-inflammatory effect: a randomized clinical trial.” Chinese medicine vol. 18,1 41. 17 Apr. 2023, doi:10.1186/s13020-023-00746-4
- Zhao, Ying et al. “Efficacy and safety of berberine for dyslipidemia: study protocol for a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.” Trials vol. 22,1 85. 22 Jan. 2021, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05028-8
- Moon, Jessica M et al. “Absorption Kinetics of Berberine and Dihydroberberine and Their Impact on Glycemia: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Pilot Trial.” Nutrients vol. 14,1 124. 28 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/nu14010124
- Feng, Xinchi et al. “Pharmacokinetics and Excretion of Berberine and Its Nine Metabolites in Rats.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 11 594852. 15 Jan. 2021, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.594852
- Och, Anna et al. “Berberine, a Herbal Metabolite in the Metabolic Syndrome: The Risk Factors, Course, and Consequences of the Disease.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 27,4 1351. 17 Feb. 2022, doi:10.3390/molecules27041351
- Yao, Jiuxiu et al. “The efficacy and mechanism of berberine in improving aging-related cognitive dysfunction: A study based on network pharmacology.” Frontiers in neuroscience vol. 17 1093180. 20 Jan. 2023, doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1093180
- Habtemariam, Solomon. “The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches.” Biomedicines vol. 8,4 90. 18 Apr. 2020, doi:10.3390/biomedicines8040090
- Derosa, Giuseppe et al. “An Evaluation of a Nutraceutical with Berberine, Curcumin, Inositol, Banaba and Chromium Picolinate in Patients with Fasting Dysglycemia.” Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity : targets and therapy vol. 13 653-661. 3 Mar. 2020, doi:10.2147/DMSO.S232791
- Demaré, Sarah et al. “Metformin as a potential therapeutic for neurological disease: mobilizing AMPK to repair the nervous system.” Expert review of neurotherapeutics vol. 21,1 (2021): 45-63. doi:10.1080/14737175.2021.1847645
- McCubrey, James A et al. “Effects of resveratrol, curcumin, berberine and other nutraceuticals on aging, cancer development, cancer stem cells and microRNAs.” Aging vol. 9,6 (2017): 1477-1536. doi:10.18632/aging.101250
- de Oliveira, Juliana Sorraila et al. “Neuroprotective effects of berberine on recognition memory impairment, oxidative stress, and damage to the purinergic system in rats submitted to intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin.” Psychopharmacology vol. 236,2 (2019): 641-655. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-5090-6
- Fang, Xinyi et al. “Research progress on the pharmacological effects of berberine targeting mitochondria.” Frontiers in endocrinology vol. 13 982145. 11 Aug. 2022, doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.982145
- Ye, Yu et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Berberine Alone for Several Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 12 653887. 26 Apr. 2021, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.653887
source https://nootropicology.com/berberine/

No comments:
Post a Comment